uv vis spectrophotometer diagram analyzing two samples|how uv vis spectrophotometer works : specialty store For example, proteins and nucleic acids absorb wavelengths in the visible light range of 240-300 nanometers (nm), pigments and dyes absorb light in the 400-770-nm range, and other organic molecules absorb wavelengths above 770-nm. . Place a cuvette with a sample into the spectrophotometer; Press "read" Set cursor mode to peak and valley under .
WEBIMPORTANTI INFORMAZIONI RIGUARDANTI I COOKIES E PLAYDAUNTLESS.COM. Utilizzando questo sito, acconsenti all'uso dei cookie in accordo con l'informativa sui Cookie di Phoenix Labs. Per maggiori informazioni e su come fare scelte in .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Hey boys! ;) See Blairebabie666's porn videos and official profile, only on Pornhub. Check out the best videos, photos, gifs and playlists from .
Schematic diagram of a fixed-wavelength, single-beam spectrophotometer. The photographic inset shows a typical instrument. The shutter remains closed until the sample or blank is placed in the sample .The principle of measurement for UV-Visible Spectroscopy or UV-Visible spectrophotometer is relatively straightforward and consists of a light source, a wavelength dispersive element, sample, and detector. Figure 1. A basic block .
If the isoprene spectrum on the right was obtained from a dilute hexane solution (c = 4 * 10-5 moles per liter) in a 1 cm sample cuvette, a simple calculation using the above formula indicates a molar absorptivity of 20,000 at the maximum . Depending on the range of wavelength of light source, it can be classified into two different types: UV-visible spectrophotometer: uses light over the ultraviolet range (185 - 400 nm) and visible range (400 - 700 nm) of .%PDF-1.6 %âãÏÓ 600 0 obj > endobj 624 0 obj >/Filter/FlateDecode/ID[0D68C31A8E0937438E797621B9C54FBD>81B828330A4A3B4A91845ACEAE23EA1A>]/Index[600 45]/Info 599 0 R . For example, proteins and nucleic acids absorb wavelengths in the visible light range of 240-300 nanometers (nm), pigments and dyes absorb light in the 400-770-nm range, and other organic molecules absorb wavelengths above 770-nm. . Place a cuvette with a sample into the spectrophotometer; Press "read" Set cursor mode to peak and valley under .
A diagram highlighting the various kinds of electronic excitation that may occur in organic molecules is shown below. Of the six transitions outlined, only the two lowest energy ones, n to pi* and pi to pi* (colored blue) are achieved by the energies available in the 200 to 800 nm range of a UV/VIs spectrum. . When sample molecules are .
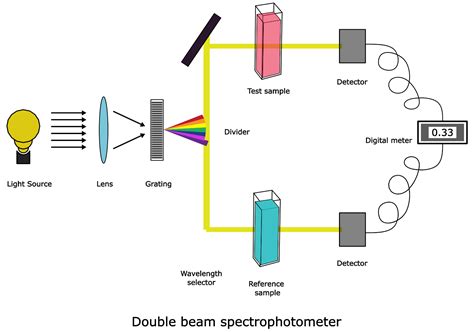
Spectrophotometry and different types of spectroscopy are the technique that involved in identifying and quantifying the amount of a known substance in an unknown medium. Spectroscopy is the most convenient method for analysis of unknown samples both qualitatively and quantitatively with a good percentage of accuracy. Different types of .Table-top spectrophotometer Beckman IR-1 Spectrophotometer, c. 1941 Beckman Model DB Spectrophotometer (a double beam model), 1960 Hand-held spectrophotometer used in graphic industry [1]. Spectrophotometry is a branch of electromagnetic spectroscopy concerned with the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a .
Dye Concentration Using UV-Vis v5 2 • Molar absorptivity – a measure of how strongly a sample absorbs light at a given wavelength; it is a physical property of a compound • Organic molecule – a molecule that contains carbon • Solute – the component in lesser amount in a solution • Solvent – the major component of a solution
UV/Vis. UV/Vis spectroscopy. atomic absorption spectroscopy. IR. infrared spectroscopy. raman spectroscopy . (\PageIndex{2}\): Examples of Spectroscopic Techniques That Do Not Involve an Exchange of Energy Between a Photon . 2 Schematic diagram of a monochromator that uses a diffraction grating to disperse the radiation. Radiation exits the .
UV-Visible spectroscopy is widely used in the field of analytical chemistry, especially during the quantitative analysis of a specific analyte. For example, the quantitative analysis of transition metal ions can be achieved with the help of UV-Visible spectroscopy. . after it passes through a sample or reflects from a sample surface. Q4 . Recall that we can draw a diagram showing the four pi MO’s that result from combining the four 2p z atomic orbitals. The lower two orbitals are bonding, while the upper two are antibonding. . Schematic for a UV-Vis spectrophotometer . sample holders are designed so that the path length is equal to 1 cm, so the units for molar absorptivity .
UV spectroscopy is a type of absorption spectroscopy in which light of the ultra-violet region (200-400 nm) is absorbed by the molecule which results in the excitation of the electrons from the ground state to a higher energy state. . Sample and reference cells. One of the two divided beams is passed through the sample solution and the second . UV-Vis Spectroscopy, short for Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy, is an analytical technique widely used in the fields of chemistry, physics, biochemistry, and . Spectrophotometry, a pivotal technique in analytical chemistry, employs various types of spectrometers to analyze samples. Delving into the details, there are primarily two types of .
UV-Visible analysis of solid samples can provide valuable information about the behavior of a material. Herein, the use of UV-Visible transmission and reflection techniques was used to demonstrate effective analysis of powder, film and curved solid samples. To aid in these analyses, a variety of accessoriesUV–Vis spectroscopy in non-destructive testing. Khalisanni Khalid, . Zaira Zaman Chowdhury, in Non-Destructive Material Characterization Methods, 2024. 15.9 Conclusion. UV–Vis spectroscopy is a cost-effective, simple, versatile, non-destructive, and analytical technique, which is suitable for a large spectrum of organic compounds and some inorganic species.
shows main parts of UV-Visible spectrophotometer [7]. 2.1.3 Applications of UV-visible spectrophotometry a. Pharmaceutical analysis: UV-visible Spectrophotometry has been widely used technique in the determination of drug concentration in pharmaceutical analysis. For example, this technique is used in the determination of etravirine in bulk and Principle of Spectrophotometer. The spectrophotometer technique is to measure light intensity as a function of wavelength. It does this by diffracting the light beam into a spectrum of wavelengths, detecting the intensities with a charge-coupled device, and displaying the results as a graph on the detector and then on the display device. Based on the number of cuvettes and beams used, UV-VIS spectrophotometer is classified into the following two types: 3.9.1 Single-Beam UV-VIS Spectrophotometer. In this type of spectrophotometer, single beam and/or cuvette is used for the analysis (Fig. 3.8). In single-beam UV-VIS spectrophotometer, a single light beam passes across the cuvette.
UV-Visible Spectrophotometer: This type of spectrophotometer utilizes light in the ultraviolet (UV) range (185-400 nm) and visible range (400-700 nm) of the electromagnetic spectrum. It is widely used for analyzing colored compounds and determining their concentration in .
This page titled 2.3: UV-Visible Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds is shared under a CC BY-NC 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Chris Schaller via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform.Guide to UV-Vis spectrophotometer uses, UV-Vis measurement techniques, and spectrophotometer applications using modern UV-Vis instruments—includes concentration measurements, conformational studies of proteins, color measurement, UV-Vis Liquids Analysis and solid sample measurements.
Sample. UV-vis spectroscopy works well on liquids and solutions, but if the sample is more of a suspension of solid particles in liquid, the sample will scatter the light more than absorb the light and the data will be very skewed. . Most UV-vis instruments can analyze solid samples or suspensions with a diffraction apparatus (Figure . A diagram of the components of a typical spectrometer are shown in the following diagram. The functioning of this instrument is relatively straightforward. A beam of light from a visible and/or UV light source (colored red) is separated into its component wavelengths by a prism or diffraction grating.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy. A diagram of the components of a typical spectrometer are shown in the following diagram. The functioning of this instrument is relatively straightforward. A beam of light from a visible and/or UV light source (colored red) is separated into its component wavelengths by a prism or diffraction grating. . If the sample .The electronic transitions of both molecular hydrogen and ethene are too energetic to be accurately recorded by standard UV spectrophotometers, which generally have a range of 220 – 700 nm. Where UV-vis spectroscopy becomes useful to most organic and biological chemists is in the study of molecules with conjugated pi systems.UV-Visible Spectroscopy. UV-Visible/NIR spectroscopy (UV-Vis Spectroscopy) can be divided into ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the spectrum, depending on the wavelengths used. since its frequency is close to the overtone frequency of many natural vibrations, weak substance-specific absorption bands can be detected.
uv visible spectroscopy images
uv visible spectroscopy block diagram
webHabitus Academia Bauru, Bauru. 905 likes · 1 talking about this. Gym/Physical Fitness Center
uv vis spectrophotometer diagram analyzing two samples|how uv vis spectrophotometer works